Gout is often the end of drinking beer. Beer can cause gout attacks and should be avoided. Are there any beers that you can still drink after a gout diagnosis?
While gout typically means you need to stop drinking beer altogether, non-purine beers are the exception as they will not cause a gout attack. Most non-purine beers are brewed by Japanese breweries, although they are often difficult to find in the U.S. Some of the most popular are Sapporo Umami Shibori, Suntory All-Free, and Stella Artois Solstice.
Keep reading to find out how what purines are, and how they can contribute to gout. There will also be a list of purine-free beers.
Topics We Cover
What are purines?
For those suffering from gout, purines are something to keep a close eye on. Since they are in nearly everything this can be a challenge, but it is manageable.
Purines are organic molecules made of a combination of nitrogen and carbon atoms. They are produced in the human body and consumed from food and drink.
The purines found in the human body (endogenous purines) are part of the DNA and RNA of a cell. When these cells die, the purines are processed into uric acid. The same occurs with purine from external sources (exogenous purines) except the purine isn’t released by cell death.
This uric acid is then either absorbed or excreted. Roughly 90% is absorbed by the body while the remaining 10% is removed.
How do purines affect gout?
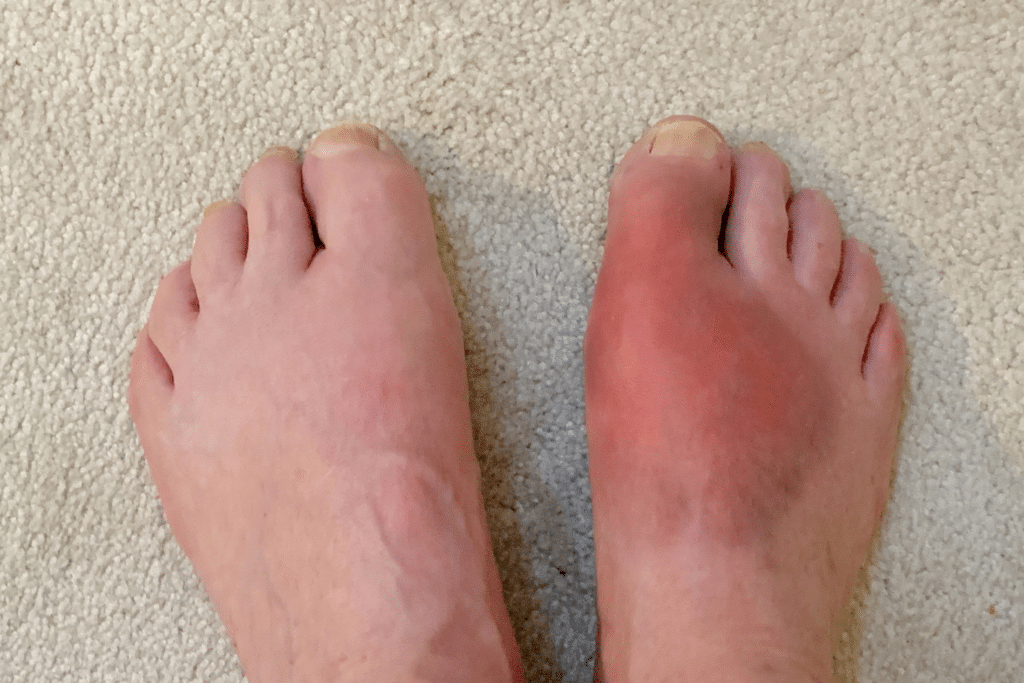
It is this uric acid that causes problems for gout. Since purines can produce uric acid, they can negatively impact those with gout.
Purine affects gout by increasing uric acid levels within the bloodstream. When purine is metabolized, it produces uric acid as a byproduct. If uric acid concentrations in the bloodstream get to be too high, they can form urate crystals in and around various joints.
The excessive concentration of uric acid is known as hyperuricemia. Since purines are produced by the human body everyone has some level of uric acid in their bloodstream. Concentrations above 7 mg/dL can begin to show symptoms of hyperuricemia.
Consuming food or drink with high purine levels can cause the bloodstream concentration to go above this level. However, hyperuricemia does not always result in gout. That said, those with gout will be negatively impacted by purines if they cause their uric acid levels to increase.
Gout flare-ups can be caused by this increase. Any spike in uric acid can do this. Sometimes it is because there is more uric acid than standard as is the case with consuming purine-rich food. Other times a flare-up is caused by impacted uric acid removal.
Does beer usually contain purines?
Not only does beer contain purines, but it is also a high purine beverage. Some beers have higher purine levels than others, but all regular beer has considerable purine levels compared to other alcoholic beverages.
A research article in Biomedical Chromatography reported that regular beer contains “225.0–580.2 µmol/L” of purines. In more familiar units, that is 25.447–65.619 mg/L.
According to the same article, some light malt beers have a lower purine content. Additionally, some microbrewed or low ABV beers may have as much as 2.5 times the purine content as regular beers.
Some of the risks associated with beer come with the specific purines present. While there are a variety of purines in beer, the most common is guanosine. This makes beer especially risky as guanosine is absorbed more quickly than other purines.
Where do the purines in beer come from?
In order to create low purine beer, we need to figure out where the purines come from.
Beer is made up of several ingredients that could be the main culprit:
- Alcohol
- Yeast
- Malt
- Adjuncts
Let’s break it down by the main aspects of beer.
Alcohol
The alcohol in beer, ethanol, is not itself a source of purines. However, it can affect how fast purines are excreted and produced.
Alcohol can reduce the rate at which uric acid is excreted which leads to greater build-up. It also increases the rate at which uric acid is produced within the body.
Yeast
On the other hand, yeast is certainly the main culprit.
Yeast, especially brewer’s yeast, is extremely high in purines. Brewer’s yeast has roughly 3000 mg of purines per 100 g.
Yeast is typically filtered out in commercial beers, but it is nearly impossible to remove all of it – not to mention the various beer styles where the yeast is left in.
Malt
Yeast isn’t the only contributing factor. The various malts that make the wort have some role to play.
Malted grains do contain purines but at a very low level. They are considered a very low purine content item.
Adjuncts
There are a lot of different adjuncts that can be added to beer. However, the common ones such as corn, rice, and wheat can be covered.
Most of the common adjuncts such as corn and rice have a very low purine content. Wheat on the other hand has a slightly higher purine content though it is still relatively low.

What happens if you drink beer when you have gout?
Beer is a hard thing to give up. If you have gout you have likely been advised to do so. It is best to give up beer entirely; however, in small amounts, it may be alright.
If you have gout and you drink a beer, you run the risk of causing a flare-up. The purines in the beer will be processed into uric acid. If the beer pushes your uric acid concentration past its threshold it will spark a gout attack.
As mentioned above, beer not only adds purines to your body but also slows the removal of the uric acid already there. Between these exogenous purines and alcohol’s effect on the human body, beer is not a great idea.
There are several methods that help to mitigate the impact of exogenous purines. These methods include medicine, plenty of water, and controlling all sources of purines. Speak to your doctor about your options if you want to continue drinking beer.

Is non-alcoholic beer better for gout?
Since standard beer is high in purines it is a logical next step to consider non-alcoholic beer. After all, it is healthier in some ways. Why not for these reasons?
Unfortunately, non-alcoholic beer is not much better when it comes to purine content. Since there is some variation in the number of purines in all beers, you may find a non-alcoholic beer that has lower levels. As a whole, they are roughly similar, however.
Non-alcoholic beer is still made using the same ingredients as alcoholic beer. As we now know, it is yeast that is the biggest problem. The same yeast is used in both alcoholic and non-alcoholic beer.
This means that the style and filtration of the beer matter more than the alcohol content.
That said, there are a few non-alcoholic beers that have also been made to eliminate purine.

Are any beers purine-free?
There are beers that have no purines in them. This is done by brewers trying to meet the needs of beer drinkers with gout. The question is how this is accomplished. Unfortunately, these brewers are not sharing their secrets with everyone.
For a beer to be purine free, it would have to be heavily processed or filtered using specific methods. Processing would involve enzymatic degradation. Filtering would involve specifically designed systems to remove the purines.
One removal method uses microorganisms to consume the purines followed by filtration to remove the microorganisms. Another method involves using a purine nucleoside phosphorylase to create a reaction that reduces purine levels.
Filtering could be accomplished using activated carbon. The activated carbon would have to follow specially designed specifications so that only the purines are removed. However, this method could result in some unwanted changes to the beer.
Purine-free beer list – the best beers for gout
The best beers for people with gout are obviously those that don’t have purines. Beers that are exceptionally low in purines can be acceptable, but they can add up after several. Keep in mind that alcohol can contribute to flare-ups even without purines in the beer.
Japanese breweries have made strides in developing purine-free beers. Unfortunately, their beers are not easily available outside of Japan. Many of the beers on this list will be Japanese.
Here are a few of the best beers for people with gout:
- Sapporo Umami Shibori
- Suntory All-Free
- Asahi Dry Zero Free
- Kirin Zero Ichi
- Stella Artois Solstice
Purine content will be listed in the description of each.
Sapporo Umami Shibori
- Style: Lager
- Brand: Sapporo Breweries
- From: Tokyo, Japan
- ABV: 0%
- Purine content: None
- Where you can find it: Japan
Suntory All-Free
- Style: Lager
- Brand: Suntory Holdings
- From: Tokyo, Japan
- ABV: 0%
- Purine content: None
- Where you can find it: Amazon
Asahi Dry Zero Free
- Style: Lager
- Brand: Asahi Breweries
- From: Tokyo, Japan
- ABV: 0%
- Purine content: None
- Where you can find it: Amazon
Kirin Zero Ichi
- Style: Lager
- Brand: Kirin Brewery
- From: Tokyo, Japan
- ABV: 0%
- Purine content: None
- Where you can find it: Japan
Stella Artois Solstice
- Style: Lager
- Brand: Anheuser-Busch
- From: Leuven, Belgium
- ABV: 4.5%
- Purine content: Low
- Where you can find it: Most liquor stores

